
Subsurface Storage
Technological Advancements &
Innovation for Hydrogen

Effective implementation of a hydrogen economy will hinge on the development of large-scale, low-cost storage solutions.
To ensure that storage is prioritized in the burgeoning hydrogen economy, GTI Energy has developed SUSTAIN H2. This collaboration was designed to accelerate the deployment of safe and cost-effective long-term underground hydrogen storage (UHS).
By leveraging scientific expertise, market insights, field experience, and industry partnerships, we aim to make significant strides in advancing UHS technology.
Key Benefits
Implement Cross-Cutting Collaboration
Minimize Redundant Research Efforts
Explore Complementary Opportunities
Save Time and Costs
Where can hydrogen be stored underground?
(Click an icon in the illustration to learn more.)
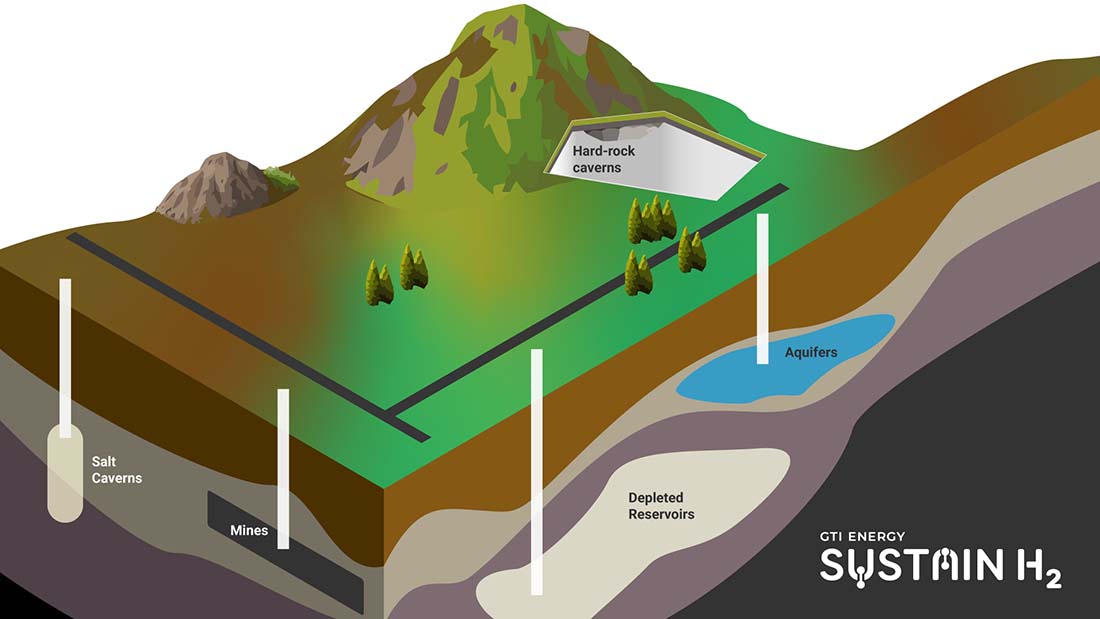
 Salt caverns are artificially created cavities in salt deposits, historically used for storing natural gas, hydrogen, and other energy resources.
Salt caverns are artificially created cavities in salt deposits, historically used for storing natural gas, hydrogen, and other energy resources.
 Previously mined rock caverns (mines), constructed in specific geological formations, can be repurposed for underground storage of gases such as compressed air.
Previously mined rock caverns (mines), constructed in specific geological formations, can be repurposed for underground storage of gases such as compressed air.
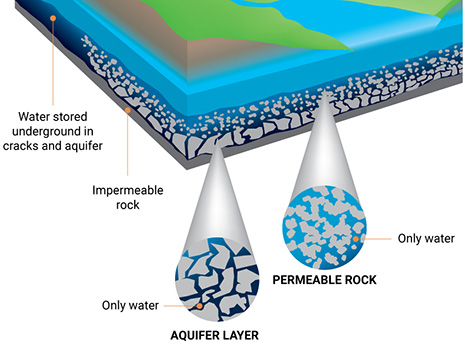 Aquifers are water-bearing sedimentary rock formations overlaid with impermeable cap rock and can be used for underground storage of natural gas or hydrogen.
Aquifers are water-bearing sedimentary rock formations overlaid with impermeable cap rock and can be used for underground storage of natural gas or hydrogen.
 Depleted oil and gas reservoirs are porous rock formations that once held hydrocarbons. After the hydrocarbons are extracted, the remaining pore space can be used for storage.
Depleted oil and gas reservoirs are porous rock formations that once held hydrocarbons. After the hydrocarbons are extracted, the remaining pore space can be used for storage.
 In the absence of other suitable geologies, underground solid rock cavities, created using conventional mining techniques, are used for storage in various applications, such as storing natural gas, compressed air, and hydrogen.
In the absence of other suitable geologies, underground solid rock cavities, created using conventional mining techniques, are used for storage in various applications, such as storing natural gas, compressed air, and hydrogen.

Salt Cavern
Salt caverns are artificially created cavities in salt deposits, historically used for storing natural gas, hydrogen, and other energy resources.

Mines
Previously mined rock caverns (mines), constructed in specific geological formations, can be repurposed for underground storage of gases such as compressed air.

Aquifer
Aquifers are water-bearing sedimentary rock formations overlaid with impermeable cap rock and can be used for underground storage of natural gas or hydrogen.

Depleted Reservoirs
Depleted oil and gas reservoirs are porous rock formations that once held hydrocarbons. After the hydrocarbons are extracted, the remaining pore space can be used for storage.

Hard Rock Cavern
In the absence of other suitable geologies, underground solid rock cavities, created using conventional mining techniques, are used for storage in various applications, such as storing natural gas, compressed air, and hydrogen.
Learn More
Contact the energy experts today

